Pakistan and the Abraham Accords: Implications for Central Asia
By Umair Jamal
Pakistan has upheld a policy of non-recognition of Israel since 1948, maintaining that diplomatic relations are contingent upon the establishment of a viable and independent Palestinian state with Al-Quds Al-Sharif as its capital. However, in late 2025, Islamabad’s mediation in the Gaza ceasefire and its conditional readiness to contribute forces to a UN-mandated International Stabilization Force have elevated its diplomatic profile with the U.S. and Gulf partners. Washington, alongside Saudi and Emirati counterparts, appears intent on expanding the Abraham Accords following credible progress toward a two-state solution. Pakistani participation would constitute a historic shift and unlock new economic corridors extending into Central Asia, enhancing regional connectivity to global markets.
Credit: Wikimedia Commons
BACKGROUND: Pakistan’s official position on Israel remains firmly grounded in support for Palestinian self-determination, a stance that resonates strongly with domestic public opinion and has guided foreign policy since the country’s founding in 1947. Pakistani diplomatic passports explicitly prohibit travel to Israel, and public discourse frequently interprets the Israeli–Palestinian conflict through the lens of historical injustice, particularly the mass displacement of Palestinians in 1948.
Anti-Israel sentiment intensified across the Muslim world, including in Pakistan, following Israel’s large-scale military offensive in Gaza, which began in October 2023 in response to the Hamas attacks. The operation has thus far resulted in tens of thousands of Palestinian casualties and extensive physical destruction across the territory.
A majority of Pakistanis regard recognition of Israel as untenable in the absence of a sovereign Palestinian state. At the governmental level, however, pragmatic considerations have increasingly shaped Islamabad’s approach amid intensifying economic pressures, including a foreign debt burden exceeding US$ 130 billion and continued dependence on international financial institutions.
In September 2025, Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif took part in a multilateral summit convened by U.S. President Donald Trump, alongside leaders from Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Qatar, to endorse a 20-point framework for a Gaza ceasefire. The initiative, which enabled hostage releases and expanded humanitarian access, marked a significant instance of Pakistan’s active mediation, coordinated through Doha and other Middle Eastern diplomatic channels.
Subsequently, in November 2025, Foreign Minister Ishaq Dar confirmed Pakistan’s willingness to contribute troops to the International Stabilization Force (ISF) established under UN Security Council Resolution 2803. He stressed, however, that the mission’s primary focus would be civilian protection and post-conflict reconstruction in Gaza rather than the disarmament of Palestinian groups. “Our job is peacekeeping, not peace enforcement,” Dar stated when questioned about the prospective deployment of Pakistani forces. This position aligns Pakistan with a coalition of eight Muslim-majority states cooperating with the U.S. to support efforts toward stabilizing Gaza.
These developments coincide with the strengthening of Pakistan’s bilateral relationship with Saudi Arabia, formalized through a mutual defense pact signed in Riyadh on 17 September. The agreement commits both states to regard an attack on one as an attack on the other and encompasses broad provisions for military cooperation and joint deterrence. It underscores the two countries’ shared strategic interests amid heightened regional instability.
Saudi Arabia has signaled its openness to joining the Abraham Accords—a framework for the normalization of relations with Israel—conditional on credible progress toward a two-state solution. In recent remarks to President Trump, Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman stated that Riyadh is prepared to participate in the Accords but seeks to secure “a clear path toward a two-state solution.”
Similarly, U.S. officials, including envoys from the Trump administration, appear to have encouraged Pakistan’s inclusion in this framework as a way to extend normalization efforts beyond the Gulf region. Although Islamabad continues to emphasize that any movement in this direction would depend on firm guarantees of Palestinian statehood, reports of backchannel exchanges suggest that discussions on the issue are evolving.
These shifts carry significant implications for Central Asia. States such as Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan are actively pursuing diversified connectivity options to reduce overreliance on Russian and Chinese infrastructure. Kazakhstan’s formal accession to the Abraham Accords in November 2025 illustrates this strategy, with the potential to strengthen its economic linkages with Israel and Western partners, particularly the U.S.
The prospective inclusion of Pakistan in the Accords could function as a pivotal connective link, but sustaining momentum would require careful management of domestic public opinion and sensitive regional dynamics.
IMPLICATIONS: If U.S. officials were to achieve their apparent objective of incorporating Pakistan into an expanded Abraham Accords framework, an outcome likely dependent on Saudi Arabia’s formal participation following progress toward a two-state solution, it would have significant ramifications for Central Asia’s economic landscape. The region’s republics, rich in hydrocarbons, uranium, and rare earth minerals yet constrained by geographic isolation, would benefit significantly from deeper integration into multimodal trade networks.
Foremost among these initiatives is the U.S.-backed India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC), which incorporates Israeli routes and seeks to streamline freight transport from South Asia through Gulf ports to Europe. Designed to circumvent traditional chokepoints such as the Suez Canal, the corridor could reduce transit times by up to 40 percent. Pakistan’s participation could extend IMEC’s eastern flank through its ports at Gwadar and Karachi, interfacing with the China–Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) to provide Central Asian exporters, particularly those in Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan. with viable southern outlets.
Such diversification would mitigate the vulnerabilities inherent in the Trans-Caspian International Transport Route (TITR), which, although operational, continues to face bottlenecks in Caspian Sea transit and persistent geopolitical frictions. In this context, enhanced Israeli technological inputs, such as advanced logistics software and desalination expertise, could improve the efficiency of these corridors, potentially generating annual trade gains amounting to billions of dollars for Central Asia by facilitating access to Mediterranean markets.
From a security standpoint, Pakistan’s prospective deployment of Islamic Security Forces (ISF) in Gaza, framed as a humanitarian stabilization mission, could serve as a model for multilateral engagement and potentially inspire analogous C5+1–style frameworks for managing Afghanistan’s borders. The Saudi–Pakistani defense pact concluded in September 2025 already signals deeper intelligence-sharing cooperation, which could extend northward to counter ISIS-K incursions threatening the frontiers of Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. Kazakhstan’s recent entry into the Abraham Accords, announced on 6 November during President Tokayev’s visit to the White House, further underscores this momentum.
Clear obstacles exist to the realization of this trajectory. Public opinion in Pakistan remains strongly opposed to normalization in the absence of Palestinian sovereignty, as demonstrated by sustained public protests and formal parliamentary resolutions. Consequently, any perceived capitulation to U.S. pressure could trigger political instability. Iranian concerns that IMEC represents an encirclement strategy, combined with its rivalry with Israel, could provoke proxy disruptions extending beyond Afghanistan into Central Asia. Moreover, China and Russia are likely to pursue countermeasures through their entrenched Belt and Road Initiative commitments, which already exceed US$ 25 billion in loans to Central Asian states. This could undermine regional cohesion and potentially exacerbate divisions, pitting Turkic-aligned states against Persian-influenced Tajikistan.
Yet a carefully calibrated strategy, linking reforms in Palestinian governance with the concurrent advancement of the IMEC corridor and an expanded role for Pakistan, could yield durable, region-wide dividends.
Israeli agricultural and water-management technologies, which have demonstrated effectiveness in arid environments, could contribute to the rehabilitation of the degraded Aral Sea basin and support the creation of tens of thousands of jobs across Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan.
Meanwhile, concrete U.S. incentives, such as the designation of Pakistan as a Major Non-NATO Ally Plus or the provision of security guarantees, could reinforce Islamabad’s willingness to resolve longstanding disputes with Afghanistan and India, facilitate full normalization with Israel, and finally enable the implementation of long-stalled connectivity projects, including the Uzbekistan–Afghanistan–Pakistan railway and the Trans-Afghan corridor.
The potential payoff could be transformative. Landlocked Central Asia would gain direct and competitive access to the warm-water ports of Gwadar, Karachi, and Mundra, unlocking billions of dollars in annual trade. This shift would also enable the region to diversify away from reliance on Russian and Chinese transit routes, thereby converting decades of geopolitical isolation into sustained economic prosperity.
CONCLUSIONS: Pakistan has conditioned recognition of Israel on the establishment of a viable Palestinian state for more than seven decades. That longstanding red line now appears to face its greatest pressure to date, as Islamabad’s effective mediation in Gaza and potential peacekeeping role have attracted praise from Washington and Riyadh. The U.S. is actively seeking to expand the Abraham Accords and aims to incorporate both Saudi Arabia and Pakistan once a credible two-state pathway is established. Should Pakistan ultimately accede, the economic payoff for Central Asia could be immediate, through faster IMEC and Trans-Caspian routes, expanded access to Gulf capital, and Israeli technology reaching the landlocked republics. Above all, this development could inaugurate a new era of integration adjacent to Central Asia that would benefit the region greatly.
Absent genuine Palestinian statehood, however, domestic opposition within Pakistan and regional resistance primarily from Iran could undermine these prospects. Ultimately, the outcome hinges on two factors: whether Pakistan can advance toward normalization with Israel without destabilizing its domestic political order, and whether the U.S. can deliver sufficient progress toward a credible and equitable two-state solution to provide Islamabad and other Muslim-majority states with the legitimacy required to take this step and unlock the region’s economic future.
AUTHOR'S BIO: Umair Jamal is a Ph.D. candidate at the University of Otago, New Zealand, and an analyst at Diplomat Risk Intelligence (DRI). His research focuses on counterterrorism and security issues in Pakistan, Afghanistan, and the broader Asia region. He offers analytical consulting to various think tanks and institutional clients in Pakistan and around the world. He has published for several media outlets, including Al-Jazeera, Foreign Policy, SCMP, The Diplomat, and the Huffington Post.
U.S.-Central Asia Summit Is No Challenge to China's Position in the Region
By Emil Avdaliani
China is closely assessing the outcomes of the November 6 U.S.-Central Asia summit and its implications for the region. From Beijing’s perspective, the relatively active U.S. engagement with this landlocked region is noteworthy but does not constitute a major geopolitical challenge. In terms of actual influence on the ground, China remains in a significantly stronger position. It enjoys geographical proximity to Central Asia and has made substantially larger investments than the U.S. is either able or willing to undertake. These investments span multiple sectors, including education, green energy, physical infrastructure development, and the extraction and processing of natural resources.
Credit: Wikimedia Commons
BACKGROUND: On November 6, Washington hosted a summit between the U.S. and the five Central Asian republics. The meeting was notable for several reasons. It marked the first time such a summit had been held at the White House and it followed President Trump’s recent bilateral meetings with the leaders of Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan.
Washington approached the summit with a pragmatic agenda. Its priorities were twofold: to secure long-term access to critical mineral resources and to strengthen the Middle Corridor as a reliable route to Central Asia that bypasses sanctioned Russian and Iranian territory.
Notably absent from the discussions were themes that had dominated earlier decades, such as the promotion of human rights, democratization, and the export of Western governance models. This marks a clear departure from the period when the C5+1 format was first introduced under President Obama in 2015. At that time, the initiative was largely designed to counter Russian and Chinese influence, rather than to promote trade and investment from the U.S.
President Trump’s regional policy is explicitly transactional. An agreement with Uzbekistan envisages approximately US$ 100 billion in investments flowing into U.S. industries over the coming years. Kazakhstan, meanwhile, has joined the Abraham Accords and concluded around US$ 17 billion in commercial agreements with the U.S., including a US$ 1 billion joint mining venture.
Cooperation on rare earths has emerged as a particularly promising area. China currently accounts for nearly 70 percent of global rare-earth production and up to 90 percent of processing capacity, which has increased Washington’s interest in diversifying its supply chains. Central Asia holds significant mineral potential, and the basis for cooperation already exists. In 2024, the U.S. and Uzbekistan signed a memorandum of understanding on critical minerals, marking the beginning of more extensive collaboration.
Historically, Central Asia has not occupied a central position in U.S. foreign policy. Limited trade ties and an excessive emphasis on democratization yielded few strategic benefits for Washington. What has changed is the broader geopolitical context. Russia’s war in Ukraine has redirected Moscow’s focus, prompting Central Asian governments to seek greater engagement with other major powers.
IMPLICATIONS: Despite the progress achieved by the U.S. in Central Asia, Washington is unlikely to marginalize China. Geography remains decisive. Any long-term American presence in Central Asia depends on secure access through the South Caucasus. The Armenia–Azerbaijan TRIPP agreement, developed under U.S. supervision, proposes a new transit corridor connecting the two states, but building the required infrastructure will take time. Even so, the Armenian route lacks direct sea access, making the existing Georgian segment of the Middle Corridor the more practical choice for large-scale trade. Ultimately, because China borders the region, logistics are simpler, and Beijing’s expanding military and security role is significant. These factors support China’s increasingly dominant position in regional trade and investment flows.
Assuming that the U.S. seeks to replace China would be a misguided analysis. Under Trump’s second term, Washington has adopted a more transactional approach, favoring a foreign policy largely devoid of human rights and democracy-promotion elements. The U.S. aims to capitalize on the willingness of Central Asian states to diversify their foreign relations, thereby enabling them to reduce their dependence on China, Russia, or other major powers.
Moreover, the U.S. is focused on a limited set of cooperative areas. Resource extraction and processing, as well as the development of east–west infrastructure that would enable exports from Central Asia, are central to Washington’s approach. By contrast, China invests across nearly all sectors of the economy. It actively pursues cooperation in education, security, and military affairs as well. Chinese companies are deeply embedded in almost every sector, ranging from renewable energy and transport to mineral extraction and processing. Uzbekistan alone has recently secured US$ 2.7 billion in Chinese investment in copper and silver projects, while U.S. processing capacity for critical minerals continues to lag far behind that of China. In September, further evidence of China’s enduring influence emerged when energy agreements worth around US$ 1.5 billion were signed during the Kazakh president’s visit to Beijing. In addition, approximately 70 commercial agreements totaling about US$ 15 billion were concluded.
It is therefore unsurprising that, following the Washington summit, China’s top diplomat Wang Yi conducted a tour of Central Asia on November 19-22 to discuss trade and infrastructure issues, underscoring Beijing’s strong position in the region. Bilateral commercial relations continue to expand. In the first ten months of 2025, trade between China and the Central Asian states increased markedly compared with the same period in 2024. In Kyrgyzstan’s case, trade rose from US$ 17.4 billion to US$ 23.6 billion, while trade between Kazakhstan and China increased from US$ 36.5 billion to US$ 39.8 billion. More modest growth was recorded in China’s trade with Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.
Central Asian states also do not seek to expand their ties with the U.S. in ways that could create tensions with China. The summit in Washington did not include cooperation on military and security issues, which are particularly sensitive for Beijing. Central Asian governments are concerned that a strong shift toward the U.S. could increase their geopolitical vulnerability vis-à-vis China. A similar logic shapes Central Asia’s relations with Russia. It is therefore notable that, following the Washington summit, Kazakhstan’s President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev visited Moscow, describing the trip as “perhaps the main event of this year.” Shortly thereafter, Russian President Vladimir Putin visited Kyrgyzstan to sign several major agreements and to reaffirm the strength of bilateral relations.
Yet China is building an extraordinarily influential geopolitical position in Central Asia due to the broad multilateral framework through which it has engaged the region. Beijing now regularly hosts summits at the level of heads of state with Central Asian countries, marking a clear elevation from earlier formats in which delegations were led by the Chinese foreign minister or other senior officials. In addition, Central Asian states are members of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization and have joined several China-led initiatives, including the Belt and Road Initiative, the Global Development Initiative (GDI), the Global Security Initiative (GSI), and the Global Civilization Initiative (GCI), as well as the more recent Global Governance Initiative (GGI).
CONCLUSIONS: The U.S. has intensified its engagement with Central Asia by elevating the level of cooperation with the region. However, its influence remains limited when compared with the range of tools available to China. Geographic proximity, together with increasingly close cooperation between Chinese and Central Asian political elites, provides a strong foundation for bilateral relations. As a result, the summit in Washington is not a major concern for Beijing but is instead viewed as part of a broader and well-established pattern in which Central Asian states engage multiple global actors through summits and major agreements. Central Asian countries also show little inclination to abandon, or even significantly reduce, their close economic and political ties with China in favor of the U.S. Rather, they continue to pursue a policy of multi-alignment, which offers greater flexibility in foreign affairs and does not generate significant concerns in Beijing.
AUTHOR’S BIO: Emil Avdaliani is a research fellow at the Turan Research Center and a professor of international relations at the European University in Tbilisi, Georgia. His research focuses on the history of the Silk Roads and the interests of great powers in the Middle East and the Caucasus.
Competition Intensifies Over Central Asia's Rare Earth Elements
By Syed Fazl-e-Haider
In pursuit of rare earth elements (REEs), U.S. President Donald Trump hosted the leaders of five Central Asian states at the White House on 6 November. China currently controls about 90 percent of global REE processing and, amid its trade conflict with the U.S., expanded export restrictions in October, constricting U.S. access to critical minerals. For an REE-dependent Washington, Central Asia offers an attractive opportunity for sourcing refined materials, particularly via the Middle Corridor linking the region to Europe through the South Caucasus. China holds nearly all rare-earth mining leases in Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan, while Russia remains the dominant actor in Kazakhstan, which possesses the world’s third-largest REE reserves. This competition for control over REEs positions Central Asia as a potential focal point of a twenty-first-century “Great Game.”
Credit: Wikimedia Commons
BACKGROUND: Rare earth elements (REEs) constitute critical minerals essential to the production of twenty-first-century high-technology systems, including smartphones, wind turbines, electric vehicles, advanced weaponry, and fighter aircraft.
In 2024, the International Energy Agency projected that global demand for critical minerals will increase fourfold by 2040. This projection has further elevated the strategic importance of resource-rich Central Asia, as Western governments intensify efforts to diversify supply chains and reduce dependence on China, which dominates global production and processing of rare earths and other rare metals.
China, which accounts for nearly 70 percent of global REE mining, introduced new export restrictions on critical rare earths and rare metals in October, intensifying global competition for control over these strategic resources. Central Asia’s substantial and largely untapped reserves of critical minerals have consequently drawn heightened attention from major powers seeking to secure alternative supply sources. The region’s significance is further underscored by the fact that it produces approximately half of the world’s uranium.
The U.S. Geological Survey classifies the 17 rare earth elements as critical minerals due to their essential role in national and economic security. This strategic importance underpins the United States’ interest in gaining access to Central Asia’s substantial untapped REE reserves. For instance, Kazakhstan possesses one of the world’s largest undeveloped tungsten deposits, a metal integral to the production of projectiles, ammunition, and other defense-related technologies in the U.S.
In March, Uzbekistan announced the discovery of deposits containing more than 30 rare metals, including tungsten, molybdenum, magnesium, lithium, and titanium. The government simultaneously unveiled plans to implement 76 projects dedicated to the extraction and processing of rare metals over the next three years, with a projected investment of US$ 2.6 billion. In July, the head of Tajikistan’s Geology Department reported the discovery of significant niobium and tantalum deposits in the country’s Rasht Valley. Both metals are considered strategically important: niobium is widely used in the aerospace and construction industries, while tantalum is essential for the manufacture of advanced electronic components.
China and Russia have been the principal importers of Kazakhstan’s critical minerals. In 2023, Kazakhstan exported critical minerals valued at US$ 3.07 billion to China and US$ 1.8 billion to Russia, according to data from the Observatory of Economic Complexity (OEC), an online trade analytics platform.
In September, Kazakhstan concluded a US$ 4.2 billion agreement with the U.S. rail manufacturer Wabtec during President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev’s visit to New York for the United Nations General Assembly. Under the terms of the deal, the U.S. company will supply 300 locomotives to support the modernization of Kazakhstan’s railway system and will additionally participate in the development of regional transport corridors linking Central Asia to Europe via the South Caucasus.
In light of China’s recent export restrictions, the U.S. is increasingly turning its attention to resource-rich Central Asia in an effort to diminish Beijing’s dominance over global critical-mineral supply chains. In October, the U.S. government facilitated negotiations between a U.S. firm and Kazakhstan’s sovereign wealth fund aimed at developing the country’s largest untapped tungsten deposits.
President Donald Trump held bilateral meetings in the Oval Office with officials from Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan as he hosted the Central Asian leaders in Washington for a high-profile summit on November 6.
IMPLICATIONS: Pursuing their own competing strategic agendas, China, Russia, the U.S., and the EU are increasingly engaged in what has been described as the “Great Game of the twenty-first century,” catalyzed in part by China’s newly imposed export restrictions on critical minerals. At the center of this geopolitical contest lies the effort to secure control over Central Asia’s vast, untapped reserves of rare earth elements (REEs).
Bound by the war in Ukraine since February 2022, Russia remains unwilling to cede influence in Central Asia, particularly as Western engagement in the region’s critical mineral sector continues to grow. At the same time, the U.S. is poised to increase investment in Central Asia’s undeveloped rare earth deposits as it seeks to reduce its dependence on China.
Leveraging its geographic proximity and extensive processing capacity, China has already established itself as the dominant actor in Central Asia’s rare earths sector. In a move to further consolidate its control over critical minerals, Beijing imposed prohibitions on the export of key processing technologies. Seeking to counter U.S. and European efforts to restructure global supply chains and diminish Chinese influence, China has also moved to secure mining rights directly in Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan.
China’s dominance in rare earth mining, processing, and refining enables it to employ these resources as a geopolitical instrument vis-à-vis Western competitors. In 2010, Beijing demonstrated this leverage by halting REE exports to Japan during a maritime dispute, disrupting Japan’s high-technology sector. Today, China’s influence in global trade, negotiations, and technological competition remains closely tied to its control over REE production and processing.
Moscow views China’s expanding role in Central Asia’s rare earth sector as a counterbalance to growing U.S. and EU influence. At the same time, Russia seeks to preserve its own position in the region, particularly in Kazakhstan’s uranium industry. Kazakhstan, the world’s largest uranium producer, depends heavily on Russia for transportation and processing, and remains a key supplier to Russia, which also holds ownership stakes in several Kazakh uranium mines.
There is substantial potential for a U.S.–Central Asia partnership grounded in shared interests in the critical minerals sector. The U.S. urgently requires access to the region’s uranium, antimony, tungsten, and other strategic minerals to strengthen its supply chains, while Central Asian states seek significant U.S. investment to develop their resource bases. Reflecting this alignment, the Trump administration has prioritized deeper engagement with the region. As Special Envoy for South and Central Asia Sergio Gor emphasized at the November summit, the president’s commitment ensures that Central Asian leaders “have a direct line to the White House” and receive the attention the region “very much deserves.”
Regional connectivity and security will be central to U.S. efforts to extract and transport Central Asia’s critical minerals. Establishing safe and reliable trade routes is essential, and Washington is likely to back corridors that bypass Russia and link the region directly to Western markets. In this context, the Middle Corridor, which circumvents Russia by connecting China to Europe through the South Caucasus, holds particular strategic appeal alongside Central Asia’s substantial mineral reserves.
China’s dominance in processing critical metals in Central Asia is facilitated by weak regulatory frameworks that allow environmentally harmful practices. For the U.S. to compete effectively, it would likewise face pressure to follow suit.
CONCLUSIONS: Geopolitically, the principal challenge for the U.S. and its Western partners is to offset the influence of China, which dominates the global REE supply chain. By expanding infrastructure investment and deepening partnerships with Central Asian states, the U.S. can position the region as a reliable partner in its rare earth supply networks.
As U.S. interest in Central Asia’s largely untapped critical mineral reserves grows, the region stands to benefit from increased investment and expanded partnerships with Washington. Such engagement would reduce Central Asia’s reliance on China and Russia and help counterbalance their influence in the region.
China’s geographic proximity and extensive REE processing capacity give it a significant advantage over the U.S. in the competition for Central Asia’s rare earth resources. Central Asian states are likely to remain dependent on Chinese and Russian supply chains unless they can surmount persistent political, infrastructural, and environmental constraints.
AUTHOR’S BIO: Syed Fazl-e-Haider is a Karachi-based analyst at the Wikistrat. He is a freelance columnist and the author of several books. He has contributed articles and analysis to a range of publications. He is a regular contributor to Eurasia Daily Monitor of Jamestown Foundation. Email:
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
.
Extending the Middle Corridor to Afghanistan: Implications for Uzbekistan
By Nargiza Umarova
Azerbaijan is strengthening its political and economic ties with the Taliban government by playing an active role in creating and developing promising transport routes to South Asia. At the forefront is the Lapis Lazuli Corridor, launched in 2018 through a joint initiative of Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Turkey, Georgia and Turkmenistan, similar to the ancient route of the Great Silk Road. The possibility of extending the corridor to South Asia is being considered, which would have geo-economic and geopolitical implications for Uzbekistan.

Credit: Wikimedia Commons
BACKGROUND: The US$2 billion Lapis Lazuli Agreement was signed by Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Turkey and Turkmenistan on 15 November 2017. The route runs from the Afghan cities of Aqina in Faryab Province and Torghundi in Herat Province, through the Caspian Sea ports of Turkmenbashi and Baku, and the Georgian Black Sea ports of Poti or Batumi, to Istanbul or Kars in Turkey, with further access to the European transport system.
The first test shipment along the Lapis Lazuli logistics chain was carried out in 2018. In January 2021, Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan and Afghanistan signed a trilateral roadmap to develop this route. However, implementation of the document was suspended due to the Taliban's seizure of power in Kabul in August 2021.
Against the backdrop of pragmatic interactions between Central Asian states — particularly Uzbekistan — and the current Afghan leadership, Azerbaijan is also seeking to strengthen its position in Afghanistan as a partner in trade, the economy, transport, and logistics.
Baku’s main priority is the Middle Corridor project, a vital logistics link between China and Europe. The Lapis Lazuli Corridor essentially extends the Middle Corridor to Afghanistan. This enables Kabul to take part in trans-Caspian shipping and to redirect some of its export cargo bound for the European market from Pakistan or Iran, to the South Caucasus and Turkey.
In 2024, Afghanistan’s total trade with the EU was approximately US$ 42 million, which is 15.9 percent higher than the previous year’s figure. Experts predict that this growth trend will continue. Meanwhile, Azerbaijan is attempting to accelerate these processes by adopting a proactive approach to its relations with the Taliban.
On July 2, 2025, on the sidelines of the Economic Cooperation Organization summit in Khankendi, Azerbaijan, Abdul Ghani Baradar, Afghanistan’s Deputy Prime Minister for Economic Affairs, met with Azerbaijani Prime Minister Ali Asadov. They emphasized Baku’s readiness to increase export and import volumes with Afghanistan. The Afghan delegation visited the Baku International Seaport, where they discussed expanding the geography of freight transport along the South Asia-Caucasus-Europe route and integrating Afghanistan into the Middle Corridor.
Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan have made significant efforts to develop the infrastructure of the Lapis Lazuli Corridor. Azerbaijan has invested approximately US$ 1 billion in two vital elements of the project: the Alat Port in Baku and the Baku-Tbilisi-Kars railway. Meanwhile, Turkmenistan constructed the Atamurat (Kerki)-Ymamnazar-Aqina railway in 2016, and connected the Afghan cities of Aqina and Andkhoy by rail in 2021. The Caspian port of Turkmenbashi is also being modernized to increase its capacity. In order to generate economic returns on their investments and reap the long-term benefits of transport service exports, it is crucial for Baku, Ashgabat and other stakeholders along the route to maximize its utilization. This justifies the idea of extending the Lapis Lazuli Corridor to Pakistan and India, which would run contrary to Uzbekistan’s interests.
IMPLICATIONS: It is assumed that the transport corridor from Europe to India via the South Caucasus, Turkmenistan and Afghanistan will become an alternative to Tashkent’s strategic plan for connecting Eastern Europe with the Indian subcontinent. This plan involves linking the Trans-Afghan Railway (Kabul Corridor) with the Northern Railway Corridor through Russia. To this end, Uzbekistan has initiated the formation of the Belarus-Russia-Kazakhstan-Uzbekistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-Indian Ocean ports transit route, which is set to launch in multimodal format soon.
The main benchmark for calculating the Kabul Corridor’s economic efficiency and feasibility is India’s growing potential for trade with Central Asian countries, the EU, China and Russia.
In the 2024 fiscal year, India’s trade turnover with the EU exceeded US$ 137 billion, with China US$ 118 billion, with Russia US$ 70 billion, and with Central Asian countries US$ 1.7 billion. The majority of Indian goods are delivered to promising markets by sea, which incurs high financial and time costs. The integration of India and Pakistan's transport space into the Eurasian road network is expected to stimulate land transportation along the South Asia-Europe axis. This shift holds great potential for the Kabul Corridor, with a projected annual cargo volume of up to 22 million tons, most of which will be in transit.
However, the extension of the Middle Corridor to Afghanistan and the development of further access to Pakistan and India will redistribute the flow of cargo from South Asian countries to Europe in favor of Turkmenistan and Azerbaijan, who are connected by the Caspian Sea. In turn, this risks diminishing Uzbekistan’s exclusive role as a trans-Eurasian transport link.
In theory, the Lapis Lazuli Corridor could be extended to Pakistan by constructing a railway line from Torghundi station on the Afghan-Turkmen border to Naibabad station, which marks the beginning of the Afghan section of the Kabul Corridor. Although this would exclude Uzbekistan from the India-EU supply chain, it would enable the Kabul Corridor to attract additional cargo from the South Caucasus and Turkmenistan. However, this advantage would not offset Uzbekistan’s loss of transit flows from the larger economic centers of Eurasia.
Connecting the Lapis Lazuli and Kabul corridors would motivate constructing the Herat-Mazar-i-Sharif railway, which would breathe new life into the long-standing Five Nations Railway Corridor project, running through China, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan and Iran. The Five Nations Route bypasses Uzbekistan, significantly reducing the distance between East and West. This will probably diminish the importance of the Southern Railway Corridor, which runs through Central Asia, Iran, and Turkey, as well as the China-Kyrgyzstan-Uzbekistan railway, which is intended to be an important component of this route.
At the same time, constructing the Herat-Mazar-i-Sharif railway could undermine the Lapis Lazuli Corridor’s competitive advantage by increasing Iranian transit. Iran already has rail access to northern Afghanistan via the Khaf-Herat route, which is used to deliver Afghan cargo to Europe. Extending the Khaf-Herat railway to Naibabad station near Mazar-i-Sharif and connecting it to the Kabul Corridor would enable Iran to divert potential cargo traffic from India and Pakistan to Turkey and Europe via itself, thereby depriving Central Asian and South Caucasian countries of transit benefits. Consequently, there is a possibility that the Lapis Lazuli Corridor could be extended to South Asia, bypassing Kabul and instead passing through Kandahar. This would stimulate the development of the western Trans-Afghan Railway along the Torghundi-Herat-Kandahar-Spin Buldak route. Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan promote the project as an alternative to the Kabul Corridor.
Russia should be considered a potential stakeholder in the extension of the Lapis Lazuli Corridor along any of the trans-Afghan routes. Moscow has already announced plans to connect with Afghanistan via the Caspian Sea, utilising Turkmenistan’s port and rail infrastructure, which would integrate Russia into the Lapis Lazuli Corridor. This would establish a connection between India and Russia, and potentially Europe, through Turkmenistan and the Caspian port of Turkmenbashi, rather than through Uzbekistan.
CONCLUSIONS: Uzbekistan’s best option for maintaining and enhancing its competitive advantages in trans-Eurasian and trans-Afghan transport is to accelerate construction of the Kabul Corridor, involving all Central Asian states financially to the maximum extent possible. Kazakhstan’s practical support for developing the Kabul Corridor is important, as connecting it to the Northern Railway Route to Europe will enable Astana to receive an additional transit flow of up to 20 million tons per year. This will preempt any potential competition from Astana and Ashgabat in developing trans-Afghan transport connections.
It would be worth proposing to Baku the joint promotion of a new multimodal corridor from India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan to Azerbaijan, Georgia, and the EU. This would stimulate the development of the Middle Corridor by increasing transport from South Asia and Afghanistan to Europe via the Caspian Sea.
Moreover, an alternative should be developed to the Five Nations Route, instead envisaging a connection between China, Afghanistan and Iran through Uzbekistan and neighboring countries. This would ensure the profitability of the Mazar-i-Sharif-Herat railway project for Tashkent.
AUTHOR'S BIO: Nargiza Umarova is a Senior Research Fellow at the Institute for Advanced International Studies (IAIS), University of World Economy and Diplomacy (UWED) and an analyst at the Non-governmental Research Institution ‘Knowledge Caravan’, Tashkent, Uzbekistan. Her research activities focus on developments in Central Asia, trends in regional integration and the influence of great powers on this process. She also explores Uzbekistan’s current policy on the creation and development of international transport corridors. She can be contacted at This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. .
The Middle Corridor Remains Supplementary to Major Trade Routes between the EU and China
By Emil Avdaliani
Although the Middle Corridor, connecting the EU and China via the Black Sea and Central Asia, has witnessed notable development in recent years, its swift expansion is constrained by both geographical barriers and the political complexities prevalent along the route. The Northern Corridor through Russia would be further consolidated should Russia achieve a favorable resolution to its war in Ukraine. While the Middle Corridor serves as a dependable link between Central Asia and the EU, it is likely to remain a complementary route to the northern Eurasian commercial highway.
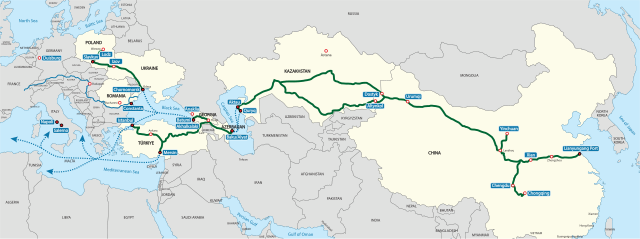
Photo source: Tanvir Anjum Adib
BACKGROUND: The Middle Corridor, also known as the Trans-Caspian Transport Corridor, extending from the Black Sea to Central Asia and western China, has gained prominence since 2022 following the onset of the war in Ukraine. Although the route had existed in practice since the 1990s and was formally inaugurated in the early 2000s, its scope remained limited due to inadequate infrastructure, geopolitical instability in the South Caucasus, and, more significantly, the appeal of the Russian route, which had facilitated trade between China and the EU. Compounding these challenges is the corridor’s multimodal nature—comprising both land and sea segments—which, despite making it the shortest geographical path between China and the EU, has ultimately rendered its operation economically unviable.
Indeed, data from the period prior to 2022 highlights this unfavorable reality: merely 2–3 percent of overland containerized freight traversed the Middle Corridor. This dynamic shifted following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, as the route became increasingly associated with geopolitical volatility, the unpredictability of Moscow, and the risk of financial loss for both the EU and China. In addition, the European Union’s imposition of extensive sanctions on Russia has further incentivized the pursuit of alternative transport corridors.
Overall, cargo traffic along the Middle Corridor increased in 2024 for railway operators in Georgia, Turkey, Kazakhstan, and Azerbaijan. For example, Azerbaijani authorities reported transporting over 18.5 million tons of goods in 2024, representing a 5.7 percent increase compared to 2023. In the case of Kazakhstan’s railways, the volume of freight carried via the corridor grew by 63 percent, reaching 4.1 million tons in 2024. Turkish and Georgian railway companies likewise experienced a rise in cargo throughput during the same year.
In late 2024, Kazakhstan unveiled plans to finance the construction of a new terminal at Azerbaijan’s Alat port. Concurrently, Astana is undertaking development efforts at the Aktau port, with authorities aiming to triple container throughput by the end of the decade. Additional recent developments similarly suggest a significant reorientation of strategic focus toward the corridor. Notably, in March, Azerbaijan hosted 24 companies for the General Assembly of the Trans-Caspian International Transport Route International Association (TITR IA) Legal Entities Union. The objective of the assembly was to raise cargo volumes along the Middle Corridor to 96,000 twenty-foot equivalent units (TEUs).
IMPLICATIONS: Thus far, the outlook for the Middle Corridor has appeared favorable. Major powers are increasingly expressing interest in the corridor’s development. In early April, the inaugural Central Asia–EU Summit was convened in Samarkand, Uzbekistan. The event was viewed as an effort to enhance the European Union’s presence in the region amid intensifying great power rivalry over Eurasian connectivity. The EU pledged a €12 billion assistance package, of which €3 billion will be allocated to the transport sector. Central Asia holds strategic significance for the EU, particularly considering the Middle Corridor’s advancement within the scope of Brussels’ Global Gateway initiative—a rival to China’s expansive Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). With improved transport infrastructure, cargo delivery times between Europe and Central Asia are projected to be halved, reaching approximately 15 days.
China is another major stakeholder, whose growing interest in the Middle Corridor is evident through both political engagement and investment initiatives. A Chinese firm is currently constructing a deep-sea port in Anaklia on Georgia’s Black Sea coast, a development that may prove instrumental in achieving the goal of capturing a 20 percent share of EU–China maritime trade by 2035. Previous efforts to build the port were hindered by domestic political disputes, but the present geopolitical environment differs, with China now actively supporting the project. Beijing has also sought to strengthen its political relationship with Georgia, culminating in the signing of a strategic partnership agreement in 2023. A similar agreement was concluded with Azerbaijan in 2024, with an upgraded version on April 23, 2025, in which China committed to enhancing the country’s Caspian Sea ports and advancing the long-delayed China–Kyrgyzstan–Uzbekistan railway. These developments collectively signal the emergence of a near-continuous corridor stretching from China’s western frontier to the Black Sea.
However, given the evolving geopolitical dynamics surrounding Ukraine—particularly the ongoing negotiations between Russia and the U.S.—the Middle Corridor may face adverse consequences. Should Russia secure substantial gains in Ukraine, its strategic influence in the South Caucasus is likely to be enhanced. This could result in the consolidation of Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan within Moscow’s sphere of influence, thereby empowering Russia to obstruct the functioning of a transit route that circumvents its territory from the south and facilitates access for rival powers into Central Asia. Potential measures at Russia’s disposal span from overt military actions to more subtle strategies, including embedding itself economically through infrastructure investments in the South Caucasus and Central Asia.
Moreover, despite the war in Ukraine entering its fourth consecutive year, this has not signaled the complete demise of the Russian route. Indeed, between 2022 and 2024, the northern corridor has continued to function as a major conduit between China and the EU. While the volume of freight transported along this route has fluctuated, it has nonetheless persisted as a vital commercial artery. Consequently, the Middle Corridor has continued to serve in a primarily complementary capacity.
This underscores the enduring viability of the northern route and should Russia–U.S. relations experience a substantial improvement; major enterprises may increasingly favor the well-established northern corridor. In contrast, the Middle Corridor continues to face constraints arising from both geographic challenges and the involvement of multiple stakeholders along its path. Infrastructure remains underdeveloped, and while intergovernmental cooperation is progressing, it still falls short of what is necessary. The true potential of the Middle Corridor is projected to reach up to 20 percent of overland containerized trade between China and the EU. However, this estimate is conditional upon several factors, including the successful completion of the Anaklia port and the expansion of the railway network across the South Caucasus.
CONCLUSION: Although the Middle Corridor has experienced considerable growth in recent years, its overall potential remains constrained. Geographic limitations, combined with persistent political complexities along the route, continue to impede rapid development. However, broader shifts in Eurasian geopolitics pose even greater challenges—should Russia succeed in concluding the war in Ukraine favorably and reconciling with the U.S., the corridor traversing Russian territory would be further solidified. This scenario does not imply that the Middle Corridor will cease to evolve. Rather, it is expected to continue expanding while remaining complementary to the northern Eurasian trade axis and functioning as a reliable conduit between Central Asia and the EU.
AUTHOR BIO: Emil Avdaliani is a professor of international relations at the European University in Tbilisi, Georgia, and a scholar of Silk Roads. He can be reached on Twitter/X at @emilavdaliani.


