India, Pakistan, and the South Caucasus Arms Race
By Syed Fazl-e-Haider
Pakistan and India, the longstanding rivals in South Asia, have instigated an arms race in the South Caucasus region. This development comes amid a broader arms supply deficit caused by Russia's preoccupation with the ongoing conflict in Ukraine. While India is deepening its military partnership with Armenia, Pakistan is enhancing the defense capabilities of Azerbaijan. Both states are actively seeking to fill the vacuum in arms procurement left by Russia's reduced presence in the region. India has aligned with Armenia, leveraging this partnership to pursue strategic connectivity projects in the South Caucasus. Conversely, Pakistan views Azerbaijan as a strategic ally, with their collaboration deemed essential for countering India in the competition for regional influence.

BCKGROUND: India and Pakistan have shared a contentious relationship since their emergence as independent states in 1947. The two states have engaged in three full-scale wars, primarily over Kashmir, a territory claimed by both. In 1998, Pakistan conducted nuclear tests shortly after India, marking a significant escalation in their rivalry. This ongoing antagonism often manifests in international forums, where the two countries accuse each other of fostering cross-border terrorism. Their rivalry extended to the South Caucasus in 2020, during the 44-day war between Armenia and Azerbaijan over the disputed Nagorno-Karabakh region.
Pakistan supported Azerbaijan during the Second Karabakh War in 2020. However, the close relationship between the two countries predates this conflict, with their cordial ties dating back to Azerbaijan's independence in 1991, following the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Pakistan was among the first nations to recognize Azerbaijan's independence, second only to Türkiye. After Armenian forces attacked Azerbaijan's Nagorno-Karabakh region shortly after its independence, both Türkiye and Pakistan strongly condemned Armenia's actions. Since then, they have consistently supported Azerbaijan’s position on the Nagorno-Karabakh issue in international forums, both politically and diplomatically. Pakistan has gone so far as to refrain from recognizing Armenia, refusing to establish diplomatic relations with the country. In return, Azerbaijan has endorsed Pakistan’s stance on the Kashmir dispute, a position that has antagonized India.
During the Second Karabakh War in 2020, Islamabad was alleged to have sent military advisers to support Azerbaijan. Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan even claimed that Pakistani soldiers were actively fighting alongside the Azerbaijani army against Armenia during the 44-day conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh. Pakistan, however, categorically dismissed these allegations, labeling them as "baseless and unwarranted." Ultimately, Azerbaijan emerged victorious in the six-week war over the disputed region.
Türkiye strongly backed Pakistan's position on Kashmir, reciprocating Pakistan’s unequivocal support for Azerbaijan during the Karabakh war. The mutual endorsements of Islamabad's stance on Kashmir by Ankara and Baku provoked concern in New Delhi. Pakistan’s support for Azerbaijan during the conflict played a pivotal role in fostering closer ties between India and Armenia in the aftermath of the war. Observing its rival’s activities during the Karabakh conflict, India responded by significantly enhancing its defense partnership with Armenia over the subsequent four years.
Meanwhile, Azerbaijan, Pakistan, and Türkiye formalized their alliance by signing the Trilateral Islamabad Declaration in 2021, underscoring their solidarity with Azerbaijan in the aftermath of the war.
IMPLICATIONS: The supply of military equipment by India and Pakistan has significantly reduced Azerbaijan's and Armenia's dependence on Russia for weapons and ammunition. Historically, both South Caucasian nations relied heavily on Russia for defense supplies, particularly in the period preceding the 2020 Karabakh War. Between 2011 and 2020, Russia accounted for 94 percent of Armenia's major arms imports, including armored personnel carriers, air defense systems, multiple rocket launchers, and tanks. Similarly, Azerbaijan depended extensively on Russian military supplies during the same period, purchasing armored vehicles, air defense systems, Smerch rockets, transport and combat helicopters, artillery, multiple rocket launchers, and tanks.
India considers Armenia a strategic partner in the South Caucasus and has consequently deepened its military ties with Yerevan. Armenia has emerged as the largest foreign recipient of Indian weapons, with defense contracts concluded since 2020 estimated at US$ 2 billion. According to a report by the Indian Ministry of Finance, Armenia has become the leading importer of Indian arms, securing deals for the purchase of Pinaka multiple-launch rocket systems and Akash anti-aircraft systems. This development reflects a significant realignment in the defense landscape of the region.
In September, Azerbaijan formally introduced Pakistan’s fourth-generation JF-17 Thunder Block III fighter jets to its air force, marking a significant milestone in defense cooperation between the two nations. This development followed a US$ 1.6 billion agreement signed in February for the acquisition of JF-17 Block III aircraft. The deal includes not only the supply of aircraft but also ammunition and pilot training provided by Pakistan. The advanced combat capabilities of the JF-17 Block III are expected to enhance Azerbaijan's military edge in the South Caucasus. Notably, Azerbaijan has requested 60 JF-17 jets, intended to replace its entire fleet of aircraft, making this the largest defense export deal in Pakistan’s history.
The defense agreements between India and Armenia, as well as those between Pakistan and Azerbaijan, have significantly diminished Russia’s position as the principal supplier of weapons and ammunition to the South Caucasian nations. This shift has been exacerbated by Russia’s ongoing war in Ukraine, which has undermined its ability to deliver weapons in a timely manner under previously signed contracts. The entry of India and Pakistan into the regional defense market has provided Armenia and Azerbaijan with an opportunity to diversify their military procurement, reducing their historical reliance on Russian defense supplies.
The entry of India and Pakistan into the South Caucasus has resulted in the formation of two rival blocs competing for regional influence. One alliance, referred to as the Three Brothers, comprises Azerbaijan, Türkiye, and Pakistan, while the opposing group includes Armenia, Iran, France, and India.
For India, Armenia holds strategic importance as a potential bridge to access the vast market of the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU). New Delhi views Armenia as a vital transit hub for connecting Indian goods to EU countries and envisions its role in facilitating bilateral or multilateral partnerships with nations such as Iran, France, and Greece to implement strategic connectivity projects in the South Caucasus.
Conversely, Islamabad considers its partnership with Azerbaijan critical for countering India's influence in the region. Azerbaijan has also emerged as a key player in the energy transit corridors connecting the Black Sea, South Caucasus, and Europe, further enhancing its geopolitical significance. This dynamic positions Azerbaijan as a strategic ally for Pakistan, particularly in the context of their shared interests in limiting India's regional ambitions.
CONCLUSIONS: Pakistan's defense cooperation with Azerbaijan and India's arms sales to Armenia are shaping new security dynamics that link the South Caucasus and South Asia. The extensive defense contracts between India and Armenia are poised to strengthen Armenia's position as a strategic ally for India in the region.
India's military partnership with Armenia is influenced by its geopolitical rivalry with Pakistan, which is actively supporting Azerbaijan's defense capabilities. Both Pakistan and India aim to secure reciprocal cooperation from the South Caucasian nations to advance their strategic interests. For Pakistan, Azerbaijan holds particular importance as a potential partner in trans-regional energy cooperation, given Pakistan's energy deficiencies. Azerbaijan's pivotal role in the energy transit corridor connecting South Asia and the South Caucasus further underscores this strategic alignment.
Conversely, India, as an observer in the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU), is working to deepen its cooperation with Armenia across economic sectors, with a particular emphasis on defense. Armenia's strategic position could also facilitate India's broader connectivity initiatives with Europe. Meanwhile, Pakistan is likely to leverage its relationship with Azerbaijan to counterbalance India's growing influence in the region, highlighting the interconnected and competitive geopolitical landscape of the South Caucasus and South Asia.
AUTHOR’S BIO: Syed Fazl-e-Haider is a Karachi-based analyst of the Wikistrat. He is a freelance columnist and the author of several books. He has contributed articles and analysis to a range of publications. He is a regular contributor to Eurasia Daily Monitor of Jamestown Foundation.
Russia’s Grip on Georgia: Will the Oligarch’s Attempt to Move Georgia Away from the West Succeed?
Vasil Sikharulidze and Malkhaz Mikeladze
December 6, 2024
Following Russia's occupation of Abkhazia and Tskhinvali post-2008, Georgia's sovereign integrity has been increasingly compromised, prompting the ruling Georgian Dream party to adopt a cautious approach towards Moscow. This shift has led to polarization within Georgian society, complicating its Euro-Atlantic integration. The country's reliance on Russian investment and trade has raised concerns about maintaining genuine independence. Russia employs various levers, including political manipulation, economic ties, disinformation campaigns, and likely interference in the parliamentary elections of 2024, in order to sustain its influence. Following these rigged elections, Georgia’s turn away from the West and toward Russia intensified rapidly.
Read Russia's Grip on Georgia (PDF)

Georgia’s Aborted EU Accession: A Political Crisis
By Laura Linderman
On November 28, 2024, the ruling Georgian Dream (GD) party explicitly announced a change in Georgia's foreign policy trajectory, despite overwhelming public opposition to turning away from European integration. Prime Minister Irakli Kobakhidze declared the party's decision to halt EU accession negotiations, rejecting talks until 2028 and refusing EU budget support. Kobakhidze asserted that Georgia would enter the EU in 2030, "with dignity" - a claim rejected by the vast majority of Georgians who view this as a betrayal of the country's pro-European aspirations.
This decision sparked nationwide protests that reflect the broad public consensus in support of European integration. Demonstrators have gathered in Tbilisi, Batumi, and cities across Georgia, condemning GD's decision and the subsequent police brutality against mostly peaceful protesters. Demonstrations have continued since the announcement, with protesters blocking streets, clashing with riot police, and facing dispersal attempts using water cannons, tear gas, and pepper spray. President Salome Zourabichvili has pledged to stay on as Georgian President, emphasizing that the illegitimate Parliament cannot elect a legitimate President.
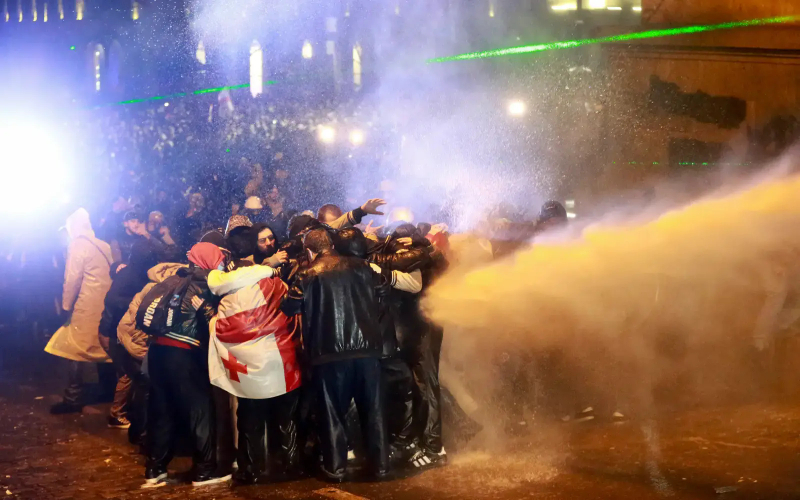
BACKGROUND: Prior to the October 26, 2024, parliamentary elections, Georgia's economy was experiencing double-digit economic growth, despite the fact that most ordinary Georgians live near poverty. This growth was fueled, in part, by financial flows from Russia, including tourism, trade, and potentially sanctions-evading investment. Russia is a significant market for Georgian products like wine, and the influx of Russian money had created a wealthy elite dependent on these financial flows. The economic growth figures helped the Georgian Dream (GD) secure support and acquiescence from some segments of the population.
This dependence on Russian money creates a conflict between Georgia's political aspirations of joining Europe and its economic realities. Despite preferential access to the EU market, Georgia did not produce much that Europe wanted to buy, while Russia was a major consumer of Georgian products. This economic reality, coupled with GD's close ties to Russia, likely contributed to the party's decision to halt EU accession negotiations, further consolidating its grip on power and jeopardizing Georgia's European future.
The protests that followed Georgian Dream's decision to suspend EU accession negotiations were fueled by a strong desire for EU integration among a distinct majority of the Georgian population. While the GD government maintained its rhetoric about commitment to eventual EU membership, its decision to postpone accession talks until 2028 provoked immediate public anger and confirmed long-standing suspicions that the government lacked genuine commitment to EU integration. The government's ratification of a Russian-style "foreign agents" law over the summer, coupled with its strategic courting of older, rural conservative constituencies more vulnerable to fears of cultural upheaval and potential conflict with Russia, further reinforced the perception that GD was prioritizing appeasement and political expediency over meaningful European alignment.
The timing of the announcement coincided with a European Parliament resolution documenting electoral irregularities. This resolution echoed widespread criticism of the elections, which were marred by concerns about the secrecy of the vote, vote-rigging, voter intimidation, and a lack of transparency, as reported by international observers. GD's decision, perceived by many as a rejection of the popular will in favor of closer ties with Russia, led to a significant portion of the population demanding immediate progress toward EU membership.
IMPLICATIONS: Since the November 28th announcement, numerous civil servants have resigned in protest, including Georgia's ambassadors to the United States, Lithuania, Bulgaria, Italy, Czechia, and the Netherlands. The Baltic states of Lithuania, Estonia, and Latvia imposed sanctions on GD founder Bidzina Ivanishvili and several high-ranking Interior Ministry officials, barring them from entering their countries. The Baltic states also condemned the suppression of protests and reaffirmed their support for the Georgian people's European aspirations. In addition to these resignations and sanctions, various sectors of Georgian society mobilized in opposition to the GD's decision. Students from universities organized marches and protests, demanding a reversal of the decision and calling on their universities to suspend classes so students could participate in demonstrations. The Georgian Trade Unions Confederation criticized GD's lack of transparency and condemned police violence against protesters. The International Chamber of Commerce in Georgia warned that halting the EU accession process would negatively impact the country's economy and investor confidence. Both major banks, Bank of Georgia and TBC Bank, and leading internet providers Magti and Silknet condemned the government's actions and reaffirmed their commitment to European integration.
The implications of GD’s decision and the subsequent protests are multifaceted and far-reaching:
-
Erosion of Democracy: GD’s actions, including the alleged election rigging and violent suppression of protests, have significantly damaged Georgia’s democratic credentials. International observers have expressed concerns about the erosion of democratic norms and the shrinking space for civil society in Georgia, especially the ratification of the Russian-style foreign agents law. The use of excessive force against protesters, including journalists, further highlighted the government's disregard for fundamental freedoms.
-
Strained EU Relations: The decision to halt EU accession has severely strained Georgia’s relationship with the EU. European officials have condemned GD's move as a betrayal of the Georgian people’s aspirations and a rejection of the country's European future. The suspension of EU budget support and the potential for sanctions against GD leaders further isolate Georgia from its European partners.
-
Strained US Relations: The US decision to suspend its Strategic Partnership with Georgia, in response to GD's halt of EU accession negotiations, signals a deterioration in US-Georgia relations and underscores US concerns about GD government's commitment to democratic values and the rule of law. By suspending the partnership, the US aims to pressure the Georgian government to reconsider its actions and to demonstrate its commitment to democratic principles. The suspension also raises questions about the future of US assistance to Georgia, which has been instrumental in supporting the country's democratic and economic development. This move could weaken Georgia's security and stability, particularly in the context of ongoing tensions with Russia. Additionally, it may embolden anti-Western forces within Georgia and undermine the pro-European aspirations of the Georgian people
-
Geopolitical Realignment and Russian Influence: The timing of Russian President Vladimir Putin's praise for GD's decision, just minutes after the announcement, has raised suspicions about potential Russian influence behind the move. The sources also highlight GD's adoption of policies, such as the "foreign agent" law, that mirror Russian legislation and have been criticized by the EU and the US.
-
Implications for Regional Stability: The potential geopolitical realignment of Georgia has significant implications for the balance of power in the South Caucasus. A shift towards Russia could embolden the Kremlin to exert more influence in the region and potentially threaten the sovereignty of other neighboring countries, particularly Armenia.
-
Economic Fallout: The halting of EU accession has created significant economic uncertainty for Georgia. The potential for reduced foreign investment and trade disruptions could severely impact the country's economic growth. While Georgia's recent economic growth has been partly fueled by Russian money, this raises concerns about economic sustainability and potential dependence on Russia. The Georgian Dream (GD) party's rejection of EU budget support will limit financial assistance and hinder development. GD's actions have damaged Georgia's international reputation and risk international isolation. Widespread protests, including strikes by schools and universities, are disrupting economic activity and further undermining investor confidence. The ongoing political instability threatens to derail Georgia's economic progress and international standing.
CONCLUSION: GD's decision to halt EU accession has triggered a nationwide crisis, revealing a stark disconnect between the ruling party and the overwhelming pro-European sentiments of Georgian citizens. While GD claims to be pursuing a "European path with dignity," its actions suggest a shift towards Russia's sphere of influence, raising concerns about the country's sovereignty and democratic future. This shift is motivated, in part, by a strategic calculation that aligns with the interests of certain political and economic elites within Georgia, who have benefitted from closer ties with Russia and favor an appeasement strategy with the North. GD has employed a range of tactics to consolidate its power, including manipulating elections, intimidating voters, and suppressing dissent, drawing parallels to the authoritarian playbook seen in countries like Hungary. The opposition's struggle to counter GD's narrative and mobilize sustained public resistance highlights the challenges facing pro-democracy forces in Georgia.
AUTHOR BIO: Laura Linderman is a Senior Fellow and Director of Programs at the Central Asia-Caucasus Institute of the American Foreign Policy Council.
Russian Elite Infighting Highlights North Caucasus Tinderbox
By Laura Linderman and Michael Hikari Cecire
In early October, Chechen leader Ramzan Kadyrov declared a blood feud against three North Caucasian federal lawmakers, accusing them of plotting his assassination amid a power struggle over the Wildberries e-commerce platform. This incident highlights the escalating tensions and fragility of power within Russian politics, revealing vulnerabilities in the Kremlin's governance amid ongoing conflicts. As regional elites assert their interests, the potential for broader instability increases, particularly against the backdrop of Russia's war in Ukraine. The situation underscores the complex interplay of patronage networks and regional autonomy that could lead to significant shifts in Russia's internal power dynamics.

BACKGROUND: In early October, Chechen strongman Ramzan Kadyrov declared a blood feud against three federal lawmakers—two Dagestani and an Ingush deputy—whom he accused of planning his assassination. The dispute is tied to control over the Russian Wildberries e-commerce website, which had been wrested by forces backed by the Dagestani and Ingush deputies against Kadyrov’s allies, culminating in a deadly shootout at the company’s Moscow headquarters. The company's contentious expansion has also led to intimidation beyond Russia's borders - in October 2024, a JAMnews editor in Georgia received threats of violence from an apparent Chechen supporter after criticizing Wildberries' entry into the Georgian market despite international sanctions. Kadyrov’s rhetoric indicates a profound willingness to use violence and intimidation, highlighting Kadyrov’s belief that he operates beyond Moscow’s control.
More broadly, the Wildberries saga highlights an ongoing scramble among Russian elites for key economic assets, and a deepening sense of growing instability throughout the contest Russian political economy arena. The North Caucasus, is a notable theater for this contestation given its historically restive and fractured contexts. Further, Kadyrov’s willingness to level threats—and the limited reaction it elicited—highlight the privileged position that Kadyrov continues to enjoy in Russia, but also the way other factions are contesting his authority. Kadyrov's comments also mark an escalation in the tensions between regional leaders and the Kremlin, illustrating the fragile balance of power within Russian politics. Kadyrov has long been known for his authoritarian rule, and this incident further showcases his leverage in the ongoing political competition among regional and federal authorities.
The ongoing conflict has drawn attention not only for its immediate violence but also for what it reveals about Russian and North Caucasus patronage networks. The region has long been characterized by real and fictive kinship affiliations that shape local governance and economic relationships. The fallout from the incident may embolden other North Caucasian factions to assert their interests in Moscow, potentially leading to further, and spiraling, destabilization. The Kremlin's haphazard approach to governance in the North Caucasus only further complicates matters. Moscow has historically relied on regional strongmen like Kadyrov to maintain stability, yet this reliance simultaneously breeds conditions for potential conflict.
Against the backdrop of an exhausting military quagmire in Ukraine, institutionally fragile security services and military apparatus made hollower by that war, and elite infighting and uncertainty as Russian President Vladimir Putin ages, the Wildberries incident reveals how Russia’s weak institutions and semi-feudal mode of control may be contributing to feedback loops of internal deterioration and instability. As the situation unfolds, it will be critical to monitor the responses from both the Kremlin and North Caucasian regional power centers, as this may foreshadow larger shifts in Russia's internal power dynamics.
IMPLICATIONS: The broader implications extend far beyond a mere violent confrontation between business interests and political factions. This event reveals profound vulnerabilities in the Russian state, which are particularly exacerbated amid its ongoing war in Ukraine.
The dynamics exposed by this recent incident suggest shifting balance between Moscow and the North Caucasus, highlighting the Kremlin’s internal fragility and the growing assertiveness of regional elites. As the war in Ukraine continues to stretch Russian resources and resolve, the Kremlin’s reliance on figures like Kadyrov to maintain control—or at least the simulacrum of control—can backfire and may kindle wider instability that can be expressed as a broader challenge to Moscow's authority.
The instability generated by Kadyrov and his patronage-based power structure, or other such triggers, could spiral into larger conflicts, not only within Chechnya but across the entire region. The interconnected nature of intertwined North Caucasian business and family groupings means that tensions in one republic can quickly spill over into others, potentially igniting violence that could further destabilize Russia's southern flank. This spillover effect extends beyond Russia's borders into the South Caucasus, as evidenced by threats against journalists in Georgia who criticize Wildberries' regional expansion. Such incidents demonstrate how Russian patronage networks attempt to exert influence through both economic penetration and intimidation in neighboring states, particularly as sanctions push Russian businesses to seek new markets
In addition, the situation signals a growing challenge to the Kremlin’s narrative of centralized control. The framented web of factional loyalties and business interests belie the formal appearance of a centralized state. As North Caucasian elites gain more visibility and influence in Moscow, the Kremlin may find itself increasingly unable to exert authority over these networks. Distracted and increasingly incapable state security structures and empowered regional elites where societal alienation from the Russian body politic is strong (or, as in the case in the North Caucasus, arguably endemic) could boost nationalist sentiments and separatist movements—particularly in the North Caucasus, which have their own historical grievances against the central government.
Finally, the likely distant but non-zero potential for federal disintegration looms. If the Kremlin's grip continues to weaken, the North Caucasus could witness a resurgence of separatist movements, echoing the conflicts of the 1990s and early 2000s. As regional elites compete for power and influence, those efforts could escalate into open conflict with each other and federal authorities—themselves fragmented patronage networks. This suggests not the need for Russia to more adequately fill the regional power vacuum, but perhaps that its tentative dominion over the region has been fundamentally illegitimate and ill-fitting.
CONCLUSION: North Caucasus instability underscores the intricate power dynamics within the region and its fundamentally contingent relationship with the Kremlin. As the Kremlin grapples with material and systemic exhaustion from nearly three years of full-scale war, the North Caucasus could be a leading indicator for generalized instability and regime weakness.
While President Putin has broadly sought to consolidate power and eliminate challenges to federal authority, the reality is Moscow—and Putin himself—have come to rely on regional elites who has operated with semi-independence and in sometimes open defiance of state structures. Kadyrov's brazen threats against federal lawmakers highlight the potential for personal and political rivalries to escalate into violence. This power struggle reveals the dissonance between Moscow's objectives and the realities on the ground, where informal networks and personalistic loyalties can often dictate political outcomes.
Moreover, the ongoing war in Ukraine is exacerbating existing tensions in the North Caucasus, making it increasingly difficult for the Kremlin to maintain stability. The region, with its historical grievances and complex interethnic dynamics, is a potential flashpoint for renewed conflict, especially as federal resources diminish. In a generalized scramble for influence and assets, the North Caucasus may be particularly prone to instability, and under certain circumstances, potentially renewed national movements or separatism. The Wildberries incident thus serves as a harbinger of potential unrest, suggesting that the Kremlin's focus on external conflicts may leave it vulnerable to internal challenges—cultivated by the very system of political economy that it has depended upon to maintain its writ.
More broadly, growing signs of instability in the North Caucasus ask questions of wider regional dynamics, including in the South Caucasus. While separated by certain geographic and especially political features (i.e., borders of the Russian Federation itself), in many respects the North and South Caucasus are a more coherent and permeable cultural space than geopolitical dynamics suggest. Narratives of ethno-linguistic segregation can be politically expedient, but often belie reality. Political controversies aside, Nakh-speaking Chechens and Ingush share a common cultural sphere in many respects with each other and the smaller but prominent Nakh and Georgian-speaking Kist and Bats communities in Georgia’s highlands. Similarly, Ossetians in the Russian Federation have far more regular interaction and exchange with a substantial Ossetian population in Georgia, not to mention with Georgians themselves. Avars and Lezgins, two of the largest ethnic groups in Dagestan, also form substantial minorities in Azerbaijan. And so on.
As such, instability in the Caucasus have dynamic effects on other parts of the Caucasus. Should the situation continue to deteriorate in the North Caucasus, it should be expected to have an effect on the South Caucasus as well, given the inherent and durable (notably, despite broader political conflicts) connectivity and interplay between north and south. Beyond cross-hatched ethnic affinities, comparable patronage dynamics exist in Azerbaijan, increasingly in Georgia, and residually in Armenia—all with business and social interests that have ties to Russia. Just as North Caucasus elites are scrambling for influence in the region and Russia’s power centers, so too are South Caucasus oligarchs and their own networks of allies and clients. Overall—what happens in the North Caucasus cannot be a strictly localized affair, and is likely to trigger instability elsewhere in Russia, and potentially spill over into the South Caucasus as well.
AUTHORS' BIOS: Laura Linderman is a Senior Fellow at the Central Asia-Caucasus Institute of the American Foreign Policy Council. Michael Hikari Cecire is an adjunct associate professor at Georgetown University’s Security Studies Program and a former senior policy advisor at the Commission on Security and Cooperation in Europe.
Georgia’s October 26th Parliamentary Election: What’s at stake and what do we expect?
By Pauline Le Grand
This Saturday, on October 26th, Georgia, will decide its future trajectory in parliamentary elections. The country stands at a crossroads and must decide whether to continue towards a European future or turn towards authoritarianism. After achieving candidate status for the European Union in 2023, the passing of the “foreign agent” law by the ruling Georgian Dream (GD) party raised concerns over the country’s democratic progression and stalled its EU ascension. The GD remains a strong contender for this election, especially in Georgia’s more conservative regions, and risks steering Georgia away from the EU for good. This election will not only test the resilience of Georgia’s democratic institutions but will also reveal the country’s broader geopolitical alignment in an increasingly polarized region.

BACKGROUND: On October 26th, Georgians will head to the polls to decide their future. This election is one of the most significant in Georgia's history as it will determine whether Georgia will remain on its European path or succumb to the Kremlin's sphere of influence. In December 2023, Georgia was granted candidate status for the European Union on the understanding that the country would work to make significant changes towards accession. Yet, since then, Georgia appears to have done just the opposite and its accession process has been frozen. In April 2024, the current government, led by the Georgian Dream (GD) party, passed the law on transparency of foreign influence, referred to as a copy-paste of Russia's foreign agent law. Civil society organizations (CSOs) receiving more than 20 percent of funds from overseas had to register on the Government's list as they were deemed to be carrying out the interests of a foreign power. The bill was first proposed in 2023 but withdrawn due to popular discontent. This year, despite promising to not revisit the law, despite even fiercer popular opposition gathering thousands of Tbilisi citizens in front of Parliament for weeks, and despite pro-European President Salome Zurabishvili's veto, the government adopted the bill on May 28th. Of an estimated 300,000 CSOs in Georgia, only 476 CSOs registered, with the others ignoring the law in protest. They preferred to wait for the government's investigation and resulting hefty fines with the hope that the upcoming election will lead to a reevaluation of the bill. The government also passed an anti-LGBTQ+ propaganda law in September as part of a legislative package 'On Protection of Family Values and Minors'. The law is a clear violation of freedom of expression and assembly. The Georgian Dream party has promised that if re-elected, it will effectively ban all opposition groups and turn Georgia into a single-party state. The GD, backed by billionaire Bidzina Ivanishvili, has been in power for the last twelve years and is determined to maintain its hold of the government. Despite the GD's apparent authoritarian turn and seeming unpopularity, it is projected to obtain a significant percentage of the vote. The question is whether it will secure enough votes for a supermajority, which would enable it to amend the constitution freely, distancing Georgia further from democracy and ultimately from the European Union.
IMPLICATIONS: In early October, the Georgian Dream launched an incredibly successful poster campaign across the country. While the capital of Georgia is relatively progressive and anti-GD, 70 percent of voters are registered outside the capital. Regional voters are overall less critical of the current government, focused on issues of employment and wages, stability and peace, and are generally culturally conservative. Regional voters have higher turnout and are therefore key to the outcome of the election and to Georgian Dream's constitutional super-majority (3/4 of Parliament).
The Georgian Dream (GD) party's rise to power was viewed by some as a positive turning point for Georgia. The party successfully ousted former President Mikheil Saakashvili, who had come to power following the 2003 Rose Revolution. Initially, Saakashvili's leadership brought significant improvements, including the removal of a corrupt elite, implementation of free-market reforms, and impressive economic growth. However, towards the end of his tenure, Saakashvili and his United National Movement (UNM) party tightened control over the political system, allowed elite corruption to spread, and expanded law enforcement powers excessively. Many felt that Saakashvili and the UNM had implemented changes too rapidly and aggressively. In contrast, GD's early years saw improvements in human rights and media freedom, along with a reduction in heavy-handed law enforcement. The party continues to benefit from lingering discontent with the Saakashvili era and fear of its potential return. GD has also cultivated support through social welfare programs, particularly pensions. Many voters worry these benefits might disappear if they don't support the ruling party. This fear is particularly pronounced in areas where electronic voting is being introduced, as some voters believe the new system compromises ballot secrecy, leading to pressure to vote for GD.
Fear remains a central and effective theme in Georgian Dream's (GD) election strategy. The mere possibility of losing pensions is often enough to drive voters to support GD. Similarly, the prospect of the United National Movement's (UNM) return motivates some Georgians to cast their ballots this Saturday. The UNM is inextricably linked to memories and fears of war.
Under Saakashvili's leadership in 2008, Russia invaded South Ossetia, a territory beginning just 40 kilometers from the capital. The 1992-1993 war with Abkhazia also lingers in the collective Georgian memory. Russia's 2022 invasion of Ukraine reignited these concerns for Georgians, who strongly support Ukraine. The fear of another conflict weighs heavily on the minds of Georgians, particularly older voters who constitute the majority of the electorate – a fear GD has not hesitated to exploit.
A week after its initial poster campaign, GD launched a new series depicting Ukrainian buildings destroyed by Russian bombs alongside intact Georgian structures. This campaign sparked online outrage, with Georgian President Salome Zurabishvili commenting on Facebook: "How desperate and pitiful must you be to shamelessly and brazenly offer your people a poster crafted in the 'forges of the KGB'! 'With dignity' towards hell!" Nevertheless, GD's message remains potent; they warn that a vote for the opposition is a vote for war. Ivanishvili even suggested apologizing to South Ossetia for the 2008 war, which he blamed on Saakashvili's government. GD also hints at the possibility of reconciliation between Georgia, Abkhazia, and South Ossetia with Russian assistance.
GD's successful fear campaigns stand in stark contrast to the opposition's apparent weaknesses. No single party emerges as particularly strong. Fragmented across four different coalitions, none offers a promising alternative. The opposition lacks connection with the regions; once outside Tbilisi, the already scarce opposition campaign posters virtually disappear. In some areas, voters have never even heard of certain opposition parties. Even in Tbilisi, those inclined to vote against GD struggle to choose a party, uncertain which might garner more votes.
CONCLUSION: This weekend's election will undoubtedly be a pivotal moment for Georgia's foreign policy orientation and liberal democracy, both within Georgia and more broadly. With a high risk of external interference, particularly from Russia, the stakes are high. Moldova's close call last weekend in the EU referendum serves as a reminder of the fragility of democracy and regional tendencies towards illiberalism. Still, the hope remains that Georgia's path will continue to align with Europe and the West, reflecting the population's overwhelming desire to join the European Union. Georgia is caught between an older population that remembers with great fear these two wars and is willing to back down to Russia and a politically active younger population who dreams of a liberal and European future. October 26th will show the rest of the world which pull is stronger today in Georgia.
AUTHOR'S BIO: Pauline Le Grand is a research intern at the Rondeli Foundation in Tbilisi, Georgia, where she researches Russia's influence in Ukraine, Central Asia and the Caucasus.


